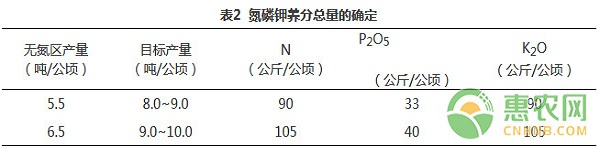
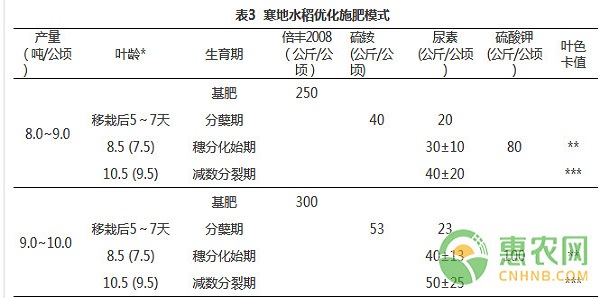
Regarding the agricultural technology knowledge articles on this aspect of cold rice, Hui Nongwang Xiaobian said that it is not too much. Everyone may not know very well. Today, I will tell you a new content, that is, the optimized fertilization technology for cold rice. I. Introduction to optimized fertilization techniques for cold rice With the promotion and application of various high-yield cultivation techniques, the yield and total output of rice in our province have been greatly improved. However, at present, there is still a lot of blindness in the fertilization of farmers in our province, especially the problem that the application rate of nitrogen fertilizer is too high and the application period is unreasonable. Among the 240 rice farmers surveyed, the maximum nitrogen application rate reached 300 kg per hectare, and it was mainly concentrated in the early stage of rice growth. Generally, the nitrogen in the base fertilizer accounted for 80% to 100% of the total nitrogen. This kind of fertilization method makes the rice ineffective tiller increase, the group quality deteriorates, the disease is aggravated, the seed setting rate is low, the rice yield is low, and the broken rice is more, which becomes a common problem in high-yield cultivation of cold rice. The optimized fertilization technology of rice is mainly based on the soil fertility and the target yield of rice to determine the total amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer. The leaf age is used to determine the growth period of rice. In the main growth period, the nitrogen fertilizer is determined according to the value of rice leaf color card. The amount of application is to maximize the demand for nutrients in the high-yield rice population at various stages. The principle of optimal nitrogen regulation in fertilization is to properly control the application rate before transplanting to jointing, and increase the application rate from ear differentiation stage to heading stage, so that the application of nitrogen fertilizer is consistent with the maximum nitrogen uptake period of rice. 2. Technical regulations for optimizing fertilization of rice in cold regions 1. Determination of the growth period of rice Nitrogen application rate and application period have a great impact on rice yield and quality. Due to the variety of rice varieties, the growth period of different varieties has obvious specificity. It is a technical difficulty to know the growth period of rice. In the optimized fertilization technology, the growth process was determined according to the leaf age of rice, which overcomes the problem that the rice growth period cannot be identified in the past, which makes the nitrogen-picuring period more accurate, and provides a scientific basis for the regulation of nitrogen fertilizer in different rice varieties according to the growth and development stage. 2. Determination and marking method of rice leaf age Rice leaf age is expressed as the number of leaves growing on the main stem. In addition to the bud sheath, the leaf on the same side as the rice husk is the first leaf. When the first leaf is completely extracted, the second leaf is tipped, the leaf age is 1; when the second leaf is completely extracted, and the third leaf is exposed, the leaf age is 2.0; if the third leaf has been finished, When the 4th leaf is being extracted, the length of the 4th leaf is compared with the 3rd leaf. If the 4th leaf length is 10% of the 3rd leaf length, the leaf age is 3.1, and if it is 50% of the 3rd leaf length, The leaf age is 3.5, and the rest of the leaf age calculations are analogous. The leaf age mark must be started before transplanting, and 10 rice plants with average leaf age are selected and marked with a marker or ink. At the time of transplanting, the marked seedlings are inserted in the observation field at a fixed point (1 point is selected at each of the opposite corners of the field, 5 lines per point, arranged in 1 line), and the mark is made. In order to ensure accuracy, one leaf age should be observed every 5 to 7 days after transplanting. One mark should be made every 1 leaf and recorded on the record book. The marking method is determined by the marker and is based on the principle that it can identify the specific leaf position of each leaf. Determine the rice growth period according to the table below. 3. Determination of total application rates of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers The total amount of nitrogen fertilizer is determined according to the yield of nitrogen-free zone. The yield of rice-free zone in our province is in the range of 5.5-6.5 tons/ha, and the yields are mostly between 8-10 tons/ha. The total nitrogen fertilizer can be determined according to Table 2. the amount. If the output of the nitrogen-free zone is low, the yield that can be obtained is also low, and there is a greater risk in pursuing higher yields. At the same time, the target yield of rice is affected by many factors. Only when the water management is good and the basic seedling number is guaranteed, the yield can be stabilized. Generally, the number of spikes per acre of the grain-type varieties is 25 to 270,000 per square meter (18 holes per square meter, 2 seedlings per hole), the number of spikes per pan number is between 34 and 360,000 (27 points per square meter, 3 seedlings per hole). According to the supply capacity of soil phosphorus and potassium and the demand for rice, the total amount of phosphorus and potassium nutrients was determined, which was determined by referring to Table 2. 4, through the leaf 4. Adjust the amount of nitrogen chase through the color card 1 Select the main stem leaves of the rice that has been completely extracted at the top, place the middle part of the leaves on the leaf color card, block the sunlight with the body, carefully compare the color of the leaves and leaf color cards, and find the leaf color level similar to the color of the leaves ( The color of the leaf color card is divided into 4 levels, and the color is from 2 to 3, 4, and 5 colors, respectively. If the blade color is in the middle of the color card 3 to 4 color level, read as 3.5, if the leaf color is close to 3 and read 3.2 deeper than 3, close to 4 and read 3.8 slightly than 4, the rest of the readings and so on. 2 Select one representative point in each plot, randomly select 10 rice varieties, compare the rice leaves with the leaf color card, and record the leaf color value. If there are 6 or more blade readings within a certain critical range, adjust the amount of nitrogen fertilizer according to Table 3. If possible, the same person reads at the same time (for example, 10 am) at each measurement. * The number of leaf ages outside the brackets for the 12-leaf rice variety, and the leaf age in parentheses for the 11-leaf rice variety; ** If there are 6 or more leaves reading 3.5~4, 15% of total nitrogen fertilizer per hectare (30~40kg urea), if the reading is close to 4 or 4, 10% of total nitrogen fertilizer (urea) 20~27kg), if the reading is close to 3 or less, the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer is 20% (urea 40~53kg); *** If there are 6 or more leaves reading 3.5~4, 20% of the total nitrogen fertilizer per hectare (40~50kg urea), if the reading is close to 4 or 4, 10% of the total nitrogen fertilizer ( Urea 20~25kg), if the reading is close to 3 or less, the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer is 25% (60~75kg urea). The above is the whole content of the optimized fertilization technology for cold rice, and the analysis is based on the actual pilot case of a certain province. The farmers who need it are welcome to make reference. Silicone Foam Dressing Bordered Silicone Foam Dressing Bordered,Silicone Foam Dressing Edging,Silicone Foam Dressing Border,Silicone Foam Dressing Frame Roosin Medical Co.,Ltd , https://www.roosinmedical.com