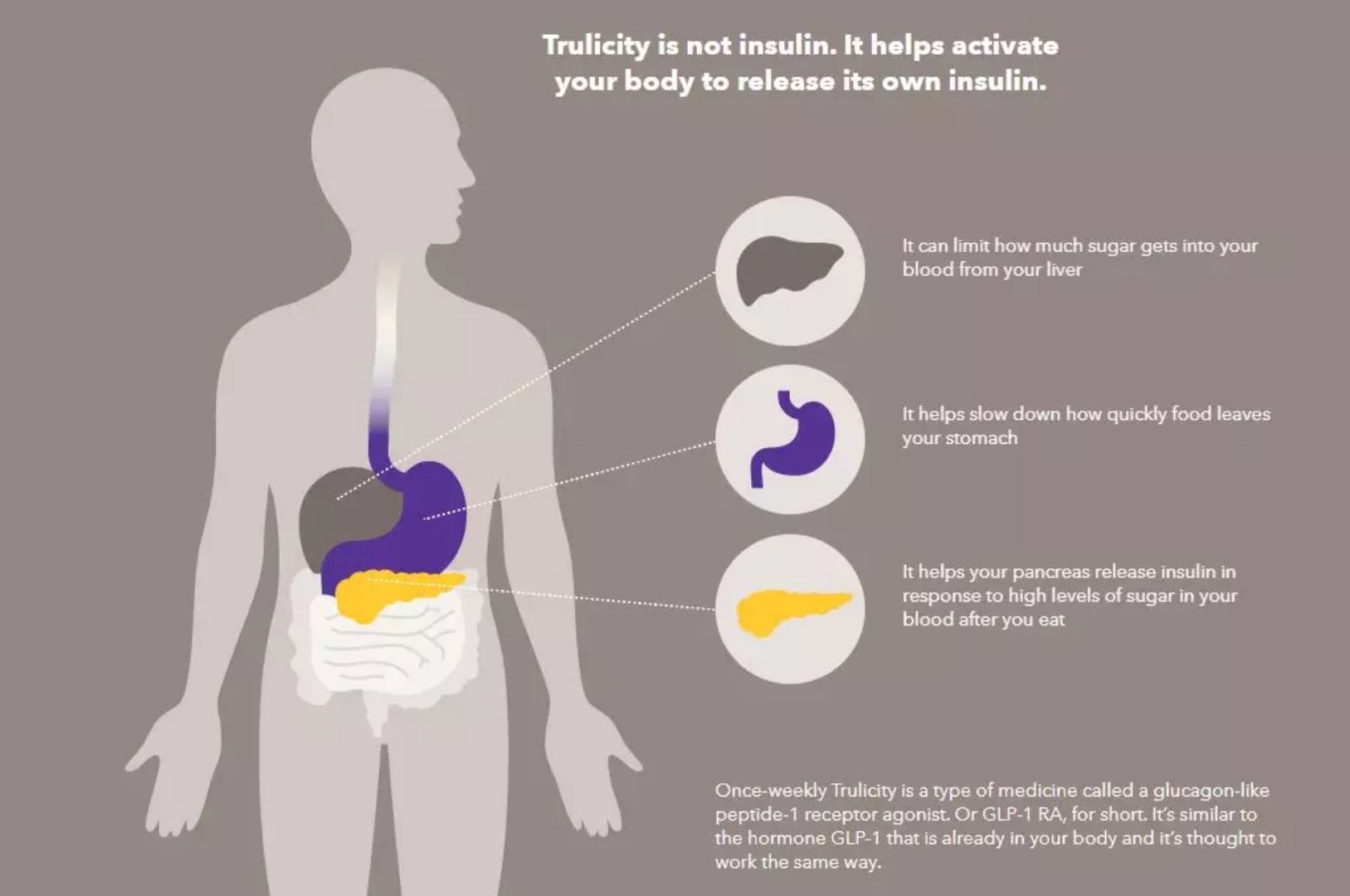
Summary of recent progress in the field of diabetes research (03.01) March 01, 2018 Source: WuXi PharmaTech 1. Significant hypoglycemic weight loss, Lilly Diabetes New Drug Phase 3 results positive Eli Lilly and Company recently published a positive result from a new Phase 3b clinical study. The new type 2 diabetes drug, Turicity (dulaglutide), significantly improved the mean blood glucose concentration (A1C) for patients over 2 to 3 months when added to the treatment of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors. The study, called AWARD-10, was recently published in the journal The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the patient's body cannot produce or use insulin properly. About 425 million adults worldwide have diabetes, and there are nearly 30 million patients in the United States alone. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes in the world, accounting for 90% to 95% of the total number of cases of diabetes in the United States. Trulicity is an Lilly Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist from Lilly. This weekly injection is approved in the United States to improve blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. AWARD-10 is a double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, 24-week Phase 3b clinical trial designed to study the safety and efficacy of 1.5 mg or 0.75 mg of Turicity in combination with SGLT-2 inhibitors. These type 2 diabetic patients (whether or not taking metformin) were not adequately controlled with SGLT-2 inhibitors. The primary goal of this study was to demonstrate that Trulicity combined with SGLT-2 inhibitors in 424 patients in eight countries significantly reduced blood glucose levels in patients compared with placebo plus SGLT-2 inhibitors. Studies showed that at 24 weeks, 1.5 mg or 0.75 mg of Tulipan was added to patients receiving SGLT-2 inhibitors to show statistically significant glycemic control (A1C was improved to -1.34% and -1.21%, respectively), while placebo The combined SGLT-2 inhibitor only improved -0.54%. In addition, significantly more patients in the Trolicity group achieved a target of less than 7% A1C and 6.5% or less (baseline 8.04%). Other results showed that 1.5 mg of Tulipan combined with SGLT-2 inhibitor resulted in a greater mean weight loss (-3.1 kg) compared with placebo (-2.1 kg). The observation in the 0.75 mg Truecity group was -2.6 kg. The most common adverse events in Trulicity are associated with the gastrointestinal tract and are consistent with previous studies. No new security issues related to Trulicity were found. ▲Trulicity's mechanism of action (Source:Trulicity) “Given some patients with type 2 diabetes who are still on the diet after diet, exercise and oral medications, they may need to increase their injection therapy,†said Dr. Brad W. Woodward, Senior Medical Director of Lilly Diabetes, “AWARD-10 indicates Trulicity, in combination with SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, may be effective and well tolerated in patients with type 2 diabetes." 2. Oral sumatripide phase 3 clinical arrival to the primary endpoint Novo Nordisk recently announced the first top-line results of the Phase 3a clinical trial PIONEER 1 in the treatment of adult patients with type 2 diabetes using oral semaglutide. Type 2 diabetes has more than 200 million patients worldwide. Insulin resistance occurs in patients, so the use of insulin alone does not work well, and other hypoglycemic agents are needed to control blood sugar. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone secreted by small intestinal cells that promotes insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion after eating to accelerate glucose metabolism while delaying gastric emptying and inhibiting appetite. Somatoglutide is an analog of natural human GLP-1 that stimulates insulin production in a glucose-dependent manner, inhibits glucagon secretion, and reduces appetite and food intake. ▲The injection version of this new diabetes drug was approved last year (Source: Labiotech.eu) PIONEER 1 is a 26-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, four-group, parallel, multicenter, multinational clinical trial comparing placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes who receive only diet and exercise therapy. The efficacy and safety of oral sumarum peptide once daily at three dose levels was compared. 703 PIONEER 1 patients were randomized to 1:1:1:1 daily, taking oral 3, 7, or 14 mg of sumaglutide or placebo. The primary endpoint was the change in long-term glycemic HbA1c from baseline at week 26. The PIONEER 1 study used two significantly different methods to evaluate the efficacy of oral somaglutide. First, the primary statistical principle. According to the latest regulatory requirements, the efficacy of oral somaglutide was evaluated without regard to treatment adherence and rescue medication. The second is the principle of secondary statistics, which assumes that all patients are compliant with treatment and that rescue medications are not administered to assess the efficacy of oral somaglutide. Based on the primary statistical principles, the trial reached the primary endpoint of the study. All three doses of oral somaglutide significantly reduced HbA1c compared to placebo. In addition, 14 mg of somaduride significantly reduced body weight compared with placebo. While weight loss was observed in the 7 mg and 3 mg doses, it did not reach statistical significance. According to the secondary statistical principle, patients treated with oral 3, 7, and 14 mg of somaduride decreased 0.8%, 1.3%, and 1.5%, respectively, from the 8.0% baseline of HbA1c, while the placebo group only decreased by 0.1%. 59%, 72%, and 80% of patients taking oral 3, 7, or 14 mg of somatoglutide reached the US Diabetes Association (ADA) HbA1c treatment target of less than 7.0%, compared with 34 patients receiving placebo. %achieve. In addition, patients taking oral 3, 7, and 14 mg of somatoglutide reduced their body mass index (BMI) by an average of 8 kg and a body mass index (BMI) of 31.8 kg per square meter, respectively, by 1.7 kg, 2.5 kg, and 4.1 kg. The patient's weight was reduced by 1.5 kg. Oral somaglutide is safe and well tolerated in this trial. “The results of the PIONEER 1 trial have been very encouraging, confirming the unprecedented oral efficacy of somaglutide reported in the Phase 2 Diabetes Phase 2 clinical trial,†said Dr. Mads Krogsgaard Thomsen, Executive Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer of Novo Nordisk: “We look forward to providing data on the remaining nine PIONEER trials this year and expect to submit regulatory reports in 2019.†3. Microsphere packaging technology maintains transplanted islet activity for up to 21 days Recently, researchers at the University of Illinois have developed a new technology that can package islet cells and provide them with oxygen and nutrients while preventing them from being attacked by recipient immune cells. This technology has the potential to increase the success rate of transplanting insulin-secreting porcine pancreatic cells into patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM). The technology also packs some drugs with islets in microsphere capsules that enhance the cell's adaptability to anoxic environments. In vitro experiments showed that after 21 days, the packaged islet cells had superior viability and function. The results were published in the journal Drug Delivery and Translational Research. T1DM is caused by the patient's autoimmune system attacking insulin-secreting cells, causing functional insulin deficiency in patients. Researchers have been exploring treatments that can treat T1DM for long periods of time to help patients avoid the pain of continuous monitoring of glucose and insulin injections. But there are many challenges in this area. First, there is a need for functional islets that will secrete insulin when they are exposed to glucose. Live islet tissue from humans is scarce, but pig tissue is well supplied, so pig insulin has been used to treat diabetes since the 1920s. Once the islets are separated from the tissue, the next major challenge is to keep them active and functional after transplantation. The first few weeks after transplantation are critical because these islet cells require oxygen and nutrients, but no blood vessels to provide them. If hypoxia occurs, it will destroy the islets. Moreover, the interaction of transplanted islet cells with the recipient immune system is also prevented. Researchers have developed microsphere capsules for biological applications such as drug delivery and cell transplantation. They use high-viscosity materials to precisely control the size and aspect ratio of capsules and produce uniform-sized microsphere capsules at high yields. With such control and high production capacity, the researchers created microsphere capsules that can hold drugs. The transplanted cells are packaged in tiny semi-permeable capsules. The size and porosity of the capsule allows oxygen and nutrients to reach the islet cells while blocking the immune cells, and provides extended release of the drug within 21 days. In in vitro experiments, the researchers packaged porcine islets and drugs in microsphere capsules and compared them to encapsulated islets without drug for the next three weeks. After 21 days, approximately 71% of the islets in the drug-packed microsphere capsules survived, while only about 45% of the drug-free microsphere capsules survived. Cells with microspheres also retain the ability to produce insulin in response to glucose, which is significantly higher than glucose levels without microspheres. Next, the researchers hope to conduct animal experiments and test their microsphere capsule technology. 4. Xeris liquid stable glucagon obtained orphan drug qualification Xeris Pharmaceuticals recently announced that its liquid-stable glucagon, a ready-to-use liquid-stable glucagon, has been approved by the US FDA for orphan drug qualification (ODD) for the treatment of hyperintestinal hypoglycemia (Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia). HH). Xeris also announced the results of Phase 2a clinical trials published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, which evaluated the use of microdose of liquid stable pancreatic hyperglycemia in patients with Post-Bariatric Hypoglycemia (PBH) The effect of the prime. HH refers to a situation in which a patient's blood glucose level becomes low or blood glucose is lowered due to excessive secretion of insulin. HH is associated with several diseases, including PBH. There are currently no approved PBH therapies. Part of the reason for the FDA's ODD is that Xeris' ready-to-use glucagon may be safer than approved drugs when used in microdoses. The results of this phase 2a clinical study (NCT02733588) demonstrate the ability to successfully treat patients with PBH with small doses of ready-to-use glucagon. The researchers used a small-dose infusion pump in combination with the information provided by the Continuous Blood Glucose Monitor (CGM) to deliver Xeris glucagon subcutaneously to the patient. Studies have shown that at a specific glycemic threshold, Xeris's ready-to-use glucagon microdose can prevent severe hypoglycemia without a rebound in hyperglycemia. ▲ Dr. Eyal Dassau, Harvard University's John A. Paulson Engineering Applications Department (Image Source: Harvard University) Dr. Eyal Dassau, one of the research directors at Harvard University's John A. Paulson Engineering Applications Department, said: "We have demonstrated in this study that this emerging technology, combined with stable liquid glucagon, can provide a way to prevent severe hypoglycemia. A new approach and may pave the way for "airbags" for people with diabetes." 5. Artificial intelligence model identifies diabetic patients with high-risk renal dysfunction Medial EarlySign recently announced the results of clinical data research in the field of diabetes, which aims to identify high-risk patients with diabetes who develop renal dysfunction within one year through machine-generated artificial intelligence. Kidney problems are one of the most common diabetes-related complications affecting approximately 20-40% of people with diabetes worldwide. Early identification and treatment may help prevent or slow the damage of the kidneys to diabetes and reduce the likelihood of future complications. The model developed by Medial EarlySign is used to predict patients at risk of kidney damage, thereby helping medical organizations provide effective interventions to reduce morbidity and mortality. Medial EarlySign's model analyzes dozens of factors in electronic health records (EHRs), including laboratory test results, demographics, medication history, diagnostic codes, etc., which predicts a high risk of renal dysfunction within one year. patient. The model examined 400,000 diabetic patients in a database of 15 million patients, separating less than 5% of the targets, and in the asymptomatic case, determined that 45% of patients would develop kidneys within a year. disfunction. This result is 25% higher than the number of patients that can be determined with the usual clinical tools. ▲ Dr. Ran Goshen, Chief Medical Officer of Medidis EarlySign (Source: Medision EarlySign) "In order to reduce the number of patients with kidney dysfunction caused by diabetes, society has invested huge cost development treatment programs," Dr. Ran Goshen, Chief Medical Officer of Mediation EarlySign, commented: "Medial EarlySign's algorithms can help decision makers, drug developers, Insurers and healthcare providers better allocate resources and obtain optimized clinical outcomes, which can help reduce the likelihood that diabetes will trigger associated end-stage renal disease (ESRD)." Reference materials: [1] New Data Show Lilly's Trulicity® (dulaglutide) in Combination with an SGLT-2 Inhibitor Improves Blood Sugar Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes [2] Novo Nordisk successfully completes the first phase 3a trial, PIONEER 1, with oral semaglutide [3] Tiny drug-delivering capsules possible sustain transplanted insulin-producing cells [4] FDA Grants Orphan Drug Designation for Xeris Pharma's Ready-to-Use Glucagon [5] Health AI Startup Medial EarlySign Predicts Which Diabetic Patients Will Suffer Kidney Damage Within One Year Original Title: Summary of Recent Progress in Diabetes Research (No. 51) Sunshade And Thermal Insulation Series Sunshade And Thermal Insulation Series,Black And White Protective Film,Aluminium Foil Double-Sided Sunscreen,Aluminum Foil Woven Fabric Insulation Changzhou Green Nets Co.,Ltd. , https://www.czglnets.com