Silicon dioxide nano particles are known as Nano Silica, it is also called Silica nano-particles. It is used particularly in the Biomedical researches. This nano silica is expected to be very much stable and to have very low level of toxicity. It is also used as concrete or cement admixture with aim to improve concrete pressure strength.
Nano Silica,Silica Nano-Particles,Concrete Nano Silica,Nano Silica SP30 Shandong Tiancheng Chemical Co., Ltd. , https://www.tianchengchemical.com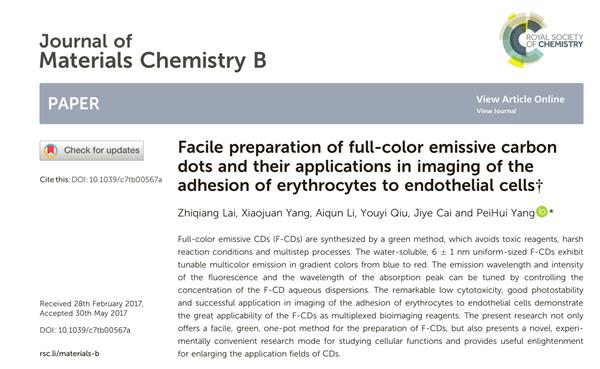



----- New fluorescent material carbon dot (f-CDS) development
The carbon dots (f-CDs) are dispersed spherical-like fluorescent carbon nanoparticles having a size of less than 10 nm. Due to its adjustable illumination range, large two-photon absorption cross section, good light stability, easy functionalization, non-toxicity and good biocompatibility, it is used in bioimaging and labeling, analytical detection, drug development, cancer nanotherapy, optoelectronics. The fields of conversion and catalysis have shown good application prospects. This also makes carbon dots an excellent alternative to semiconductor quantum dots, polymeric nanomaterials, and organic fluorescent materials.
However, how to study whether these materials are toxic to cells has not been a good method of verification. In February 2017, Mr. Yang Peihui from the School of Chemistry and Materials of Jinan University, with the real-time label-free and damage-free imaging technology of 3D cell Explorer, the leading technology product of Nanolive. Successfully published an article in The Royal Society of Chemistry; the article uses 3D cell explorer real-time non-invasive label-free imaging to quickly analyze the adhesion of red blood cells to endothelial cells, and verified that f-CDs have no effect on cells, novel and unique. The data fully demonstrates the potential of CDs for non-toxic and fluorescent imaging applications.
experimental design:
1. Preparation, index and performance identification of f-CDs
2. Intracellular imaging luminescence identification of f-CDs
3, 3D cell explorer no damage and no label analysis of red blood cell and endothelial cell adhesion
4, f-CDs toxicity test: observe the effect of CDs on the adhesion of red blood cells and endothelial cells
1. CDs preparation, index and performance identification
Preparation of carbon dot material : 0.3 g of L-tryptophan was dissolved in (100 ml, 0.05 M) aqueous sodium hydroxide solution; platinum plate was used as an anode and cathode insertion solution, and the two electrodes were subjected to electrification treatment for 2 hours to obtain a brown solution. The membrane was dialyzed against deionized water for 24 h. Purified carbon dots were obtained after vacuum freeze drying. Equipment such as Heraeus spectrometers and transmission electron microscopes verify that the carbon spot size is about 5-7 nm.
2. Identification of CDs in intracellular luminescence imaging
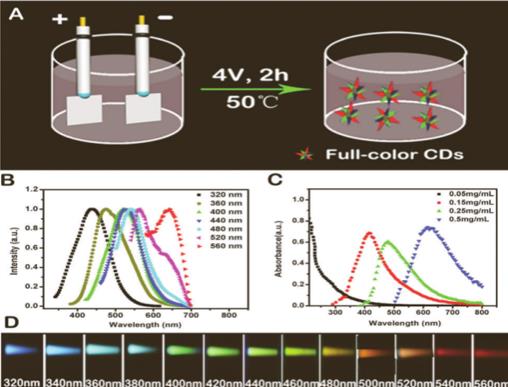
Cells that were grown to 85% homogeneity by MMT were added to F-CDs at concentrations of 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 mg / mL, respectively, and the cells were detected to emit blue, green, and red fluorescence wavelengths. Incubate at 37 degrees for 30 min for multicolor fluorescence imaging observation.
3 , 3D cell explorer label-free imaging system to observe the adhesion of red blood cells and endothelial cells
Experimental operation : 1. Endothelial cells were treated with H2O2 for 12 h, and MTT was 50 mM for MTT.
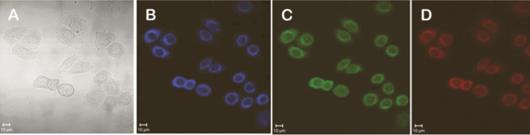
Experimental verification : Nanolive label-free imaging system through-to-fault scanning and holographic imaging technology, 3D imaging of cells, 360-degree rotation analysis of 3D images, observed that red blood cells and non-adherent endothelial cells hardly adhere, after cell damage, red blood cells to cells Endothelial cells produce a strong tendency to adhere.
A endothelial cells; B red blood cells; C red blood cells and normal endothelial cells; D red blood cells and damaged endothelial cells
4. CDs toxicity verification: observation of the interaction between red blood cells and endothelial cells
As the concentration of H2O2 increased, the degree of endothelial cell damage increased, indicating that the adhesion of red blood cells to endothelial cells was enhanced, which was consistent with the observation of the previous Nanolive label-free and damage-free imaging system.
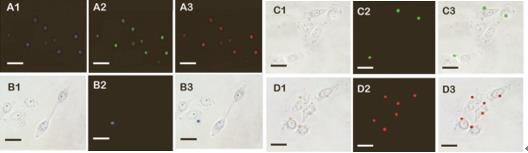
A map first processed red blood cell imaging with F-CDs, showing blue, green, and red fluorescence, respectively.
B, C, D map, labeled red blood cells were co-incubated with H2O2 treated cells, and the adhesion effect was observed.
RESULTS: In this study, the non-invasive study of the nano-dimensional 3D cell exlporer real-time label-free imaging system found that the adhesion of red blood cells to damaged endothelial cells was positively correlated with the degree of endothelial cell damage, and then the whole-wavelength fluorescence f-CDs were added to verify the pair. The adhesion of these two cells showed that the adhesion of the two cells was not affected after the addition of f-CDs, and the innovative data obtained by Nanolive's non-invasive imaging technique was used to demonstrate the emission obtained by electrochemical methods. The full-wavelength fluorescence of f-CDs provides an irreplaceable effect on the non-toxicity of cells; the provided 3D structure and quantitative analysis of label-free cell interactions provide reliable data support for subsequent studies!
Expanded application : This document makes full use of Nanolive 3D cell exlporer's real-time non-invasive, label-free technology to explore the function of new materials and drugs, and verified by fluorescence imaging. Unique data; but with two systems, there is some trouble in operation and control, nanolive's latest nanolive 3D cell exlporer–Fluro, integrating holographic imaging technology, 360-degree rotating source tomography and fluorescence imaging technology into In one, simultaneous label-free 3D cell imaging and fluorescence-labeled imaging can be achieved, images can be seamlessly integrated, and fluorescence imaging can be directly upgraded to the 3D layer, without labeling, for cells such as carbon dots f-CDs in cells The subcellular organelles and the cell level at the cell level are precisely positioned to further analyze the application of nanomaterials, and the results are more convincing!
3D Cell-Explorer-flu innovative technology products have the following advantages in the fields of life sciences and chemical materials:
v Integrated holographic technology combined with 360-degree rotational tomography and fluorescence imaging
v Real-time unmarked 3D holographic imaging seamlessly integrated with fluorescence imaging
v Nanoscale 3D cell structure observation subcellular organelle
v Any digital dyeing based on physical refractive index
v Unmarked nanoscale resolution, up to 75nm
v Ultra-high speed 3D imaging: 2-second 96-segment tomography and 3D image rendering
v Integrated platform incubation system for time-Lapse
v 3-channel fluorescence imaging, 7-channel unlabeled imaging, up to 10 simultaneous label detection
v Nanomaterials, protein, nucleic acid molecular organelles and cell-level precise positioning
We look forward to your help in the field of scientific research!
Purui Maddy (Beijing) Laboratory Technology Co., Ltd.
Address: Room 401, International Business Incubation Center, No. 9 Kexing Road, Fengtai District, Beijing
Sales department
After sales service 400
Email: Website: