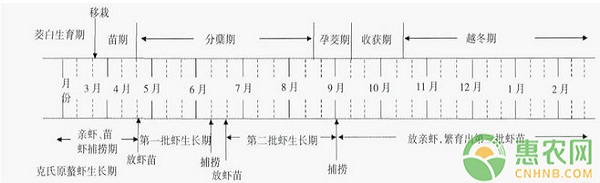
Today, we are going to learn a new breeding model, that is, the green production technology of the “one squid and three shrimps†ecological breeding model, èŒ refers to èŒ white, shrimp refers to the original crayfish, that is, crayfish. This model can make the best use of the space and water resources conditions of the Baitian area, and reach the anniversary. Baitian can harvest one season of white peony and three batches of Procambarus clarkii (2 batches of Shrimp in the sorghum, 1 batch of sorghum shrimp), and realize one water and two Use, the goal of more than one field. This model is also a form of breeding in the above-mentioned model. Relevant experts introduce the technology of each production link of the breeding model, in order to develop a comprehensive breeding model for paddy fields in the Lixiahe area of ​​Jiangsu Province, and realize the dual-use, A field of green production provides a technical reference. 1 Field supporting project and water level regulation 1.1 supporting projects 1.1.1 Field Specifications In order to facilitate the mechanization of the field, the field specifications of “one squid and three shrimps†have the characteristics of “three majors†such as large field block, large ring ditch and large glutinous rice noodles. The suitable area of ​​the field is 2~3hm2, and an annular groove with a width of 3~4m and a depth of 0.8~1.0m is excavated along the inner side of the field. In the middle of the large surface above 3hm2, the middle of the rafter is to be separated or excavated. The “Ten†shaped field ditch is connected with the ring ditch. The width of the ditch is 2~3m and the ditch depth is 0.8~1.0m. 1.1.2 irrigation and drainage Separate water conservancy facilities In order to maintain good water quality in the “one squid and three shrimps†comprehensive breeding field, it is necessary to establish relatively independent, irrigation and drainage water facilities to avoid the pollution of the discharged water and the water source. The water inlet and outlet are sealed with a dense filter to prevent the eggs or larvae of harmful organisms from entering the field, and the wild crayfish in the field. Irrigation: Establish water diversion facilities such as pumping stations and canals (pipes) to divert clean water into the fields; Drainage: Generally, through the culverts and canals (tubes), the inferior water in the “one squid and three shrimps†comprehensive breeding field is discharged into the special The constructed wetlands are purified for recycling. 1.1.3 Build anti-escape facilities Polyethylene plastic film is used as anti-floating net around the comprehensive breeding field. The bottom of the anti-fleeing net is buried in the soil about 10cm, the upper part is about 30cm high, and the outer side of the anti-escaping film is fixed by wooden stakes. The spacing of the piles is 1.5~. 2m. 1.2 water level control technology The water level is regulated according to the principle of “shallow-deep-shallowâ€, that is, the shallow water level of 5-10 cm at the time of 3-5 months is conducive to the white seedling growth and growth and the capture of the pro-prawn and seedling shrimp of the original crayfish; 6-8 months The deep water level of 40-80cm can promote the growth of white and K. serrata; the shallow water level of 20~30cm in September-November is conducive to whitening and shrimp catching. After wintering, the water level of the crayfish and the original crayfish should be shallow to 2/3 of the depth of the ditch. The first year of January and February is the lowest temperature. At this time, the ring should be full of water and the surface should have a water depth of 30-40 cm. . 2 space-time coupling technology The white cultivar was selected as “Lu'an èŒâ€, and the planting distance was 90cm×40cm, one per hole, and the basic seedling was about 1850/667m2. The temporal and spatial coupling of the white stalking in the “one squid†model, the shrimp culture in the two seasons of the original crayfish and the shrimp breeding in the winter season are shown in the figure. Spatio-temporal coupling of the ecological breeding model of the picture "One squid and three shrimps" 2.1 The first batch of shrimps In the middle and late March, before or after the transplanting, the plants were planted with water plants such as Elodea and Hydrilla verticillata in the gully and on the surface of the raft, and the water was disinfected in time. When the seedlings are transplanted in the middle of April or when the stems and leaves of the regenerated seedlings reach 25 to 30 cm, the larger-sized shrimp seedlings of 150 to 200/kg are placed, and the seedling density is preferably 10,000/667 m2. Due to the advanced breeding time, the temperature is moderate, the disease is less, and the growth is fast. The shrimps in the first round can be marketed for about 60 days, and then harvested in the first half of June. The yield of the original crayfish is 150. ~200kg/667m2. 2.2 The second batch of shrimps After the first batch of shrimps were harvested, the second batch of shrimps was placed in mid-June for the second round of shrimp farming. When the shrimp seedlings are tight, the shrimp seedlings can be temporarily raised in the purse seine of the shrimp ditch in the middle of May. After the first batch of shrimps are harvested, the seine nets are removed and the shrimps are released in the whole field. The second batch of shrimp stocking density is generally 6 000 ~ 7 000 / 667 m2. Since the second round of prawn is in the high temperature season, the general disease occurs more and the survival rate is relatively low. The water quality should be regulated in time to prevent and control the disease. The second round of prawn is generally harvested in July and September, and the total period is correspondingly extended. The output can also reach 80-120kg / 667m2. 2.3 The third batch of post-mortem breeding The white is generally harvested around October. In November, the shoots and leaves of the shoots are removed, and they enter the wintering period and regenerate in March of the next year. Using the winter leisure field after the whitening winter, the broodstock is used to breed a batch of shrimp. Generally, at the end of September, 70-75kg/667m2 of broodstock grouped in different places is placed in the shrimp ditch, and the ratio of male to female is 1:1. Naturally, it is wintering, so that they can be mated in the cave, and they will emerge in the end of March and early April. It can produce 80,000 to 100,000 tails/667m2 of shrimp seedlings. If the medium-sized seedlings are 400 tails/kg, the seedling yield is 200-250kg / 667m2. At this time, the broodstock was caught in time to prevent the broodstock from preying on the shrimp seedlings, and the shrimps were successively harvested and sold to the farmers, and 10 000/667 m2 of the culture was kept, and a new round of prawn co-production was continued. In the winter nursery seedlings, water should be kept in the ring ditch, and when the temperature is the lowest in January-February, the surface of the clams is 30-40 cm, and disinfected with quicklime once. 3 Green fertilization technology According to the actual production, according to the “six-in-one†fertilization measures, the “one-three-three-shrimp†green fertilization technology is introduced as follows. 3.1 base organic fertilizer Base fertilizer application of organic fertilizer 500kg / 667m2 (mainly dry duck manure). The nutrient contents of N, P2 O 5 and K 2 O in dry duck manure were determined to be 1.69%, 1.31% and 0.79%, respectively, and the combined application of the field was N8.45kg / 667m2, P 2 O 5 6.55kg / 667m2 and K 2 O3.95kg/ 667m2. 3.2 sets of shrimp excretion and fertilization The wintering broodstock lives in the cave and is basically in hibernation, and there is no bait, regardless of its excretion. The excretion of shrimp in the two stages of sorghum is estimated by the amount of feed. In the two stages of shrimp culture, 30 kg / 667 m2 of shrimp seedlings were put into the farm. After 60 days of breeding, 150 kg/667 m2 of shrimp were harvested. The daily feed amount was calculated as 5% of the weight of the shrimp. The total feed volume was 540 kg/667 m2, of which 240 kg/ The 667m2 feed is converted into adult shrimp weight, and the actual 300kg/667m2 shrimp feed is converted into fertilizer, namely shrimp excrement and residual bait. The feed containing N and P 2 O 5 were 4.80% and 2.06%, respectively. The combined application of the field is divided into N14.40kg /667m2 and P 2 O 5 6.18kg / 667m2. 3.3 Irrigation ponds eutrophicated water The irrigation amount of eutrophic water in the pond was 300t / 667m2. The average TN, TP and TK of the eutrophicated water in the culture pond were determined to be 9.73 mg / L, 0.77 mg / L and 4.53 mg / L, respectively. The total nutrients of P and K are 2.92kg/667m2, 0.23kg/667m2 and 1.36kg/667m2 respectively. The equivalent application of èŒç™½ç”°N is 2.92kg/667m2, P 2 O 50.53kg/ 667m2 and K 2 O 1.64kg / 667m2. 3.4 Balanced fertilization requirements According to the demand characteristics of white nutrients, the production of 1500kg/667m2 meat emulsion requires N25kg /667m2, P 2 O 5 12kg / 667m2 and K 2 O15kg/ 667m2. In view of this demand, the total fertilization measures are applied to the nutrients of the three fields. For N 25.77kg/667m2, P 2 O 513.26kg/667m2 and K2 O 5.59kg/ 667m2, nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients have been met, and K 2 O9.41kg / 667m2 is required to be added, which is equivalent to 18.64kg/667m2 sulfuric acid. Potassium. At the end of the tillering stage, potassium sulfate was 8.64 kg/667 m2, and potassium sulfate was applied before the booting stage at 10.0 kg/667 m2. In addition, considering the slow release of nutrients in the organic fertilizer application, or the inability to be fully utilized in the season, the application of the sustained-release compound fertilizer (15-15 - 15) 5kg/667m2 is guaranteed in the application of the base fertilizer. Ensure that the white yield is basically unaffected. Compared with conventional fertilization, the green fertilization scheme saves 60% of chemical fertilizer application, and at the same time ensures that the chalky yield is basically unaffected. 4 Green pest control technology for pests and diseases 4.1 white The green prevention and control of the pests and weeds in the “One Shrimp and Three Shrimp†model follows the principle of the “four-in-one†pest control system, and mainly implements the concept of prevention and comprehensive prevention. The key technical measures are Agricultural control, ecological control, physical control and biological control. Agricultural control: choose the "Lu'an" variety of high quality, high yield and multi-resistance; clean the pasture in winter, remove the straw on the pier or feed the cattle and sheep, reduce the source of the overwintering insects and the infection of the germs of the leap year; Before the larvae of Daphnia and Chilo suppressalis larvae, drain the field water, wait for the peak of the pupation, fill the deep water 10~15cm, drain after 3~5d, kill the cockroaches; once every 2 years, carry out the water and drought rotation Wait. Physical control: 1 frequency vibration insecticidal lamp is equipped for every 3hm2. Adjust the solar light control switch to light up at 8: 00 in the evening to 3: 00 in the morning when the insects are active, to kill the adult mites and adults, and use the yellow sticky board to trap the long green planthoppers and mites. Ecological control: Insert one aphid trap every 200m2, set the piece and replace the lure in time. Biological control: construct a system of common shrimp and shrimp, use shrimp to feed on pests and weeds in the field; use biological pesticides: use 8 000 IU / mg Bt wettable powder 100g / 667m2 to control stem borer, giant salamander, vertical leafhopper, etc.; 20% triadimefon (2 500 times solution) to prevent rust; spray with 20% tricyclazole wettable powder 500 times solution to control flax leaf spot; use 5% jinggangmycin (1000 times solution) to control sheath blight . Using the above four-pronged green prevention and control technology, the prevention and control rate of the pests and diseases of the “one squid and three shrimps†comprehensive species can reach 86%, and the control rate of grass damage is 91%. Compared with conventional control of pests and diseases of white field, the chemical pesticide reduction rate can reach more than 70%. 4.2 Procambarus clarkii Common diseases of Procambarus clarkii include rotten rot disease, black shank disease, rotten tail disease, polyglycosis and ciliate disease, and follow the principle of “prevention first, prevention and control combinationâ€, and then dry the field after finishing the field. Keep the shallow water level in the ring groove, sprinkle lime 100g / m2 or bleach powder 10g / m2 disinfection, while killing wild fish. After the shrimps are stocked, the disinfectant is sprayed on the deep ditch water in the field at intervals of about 20 days. The commonly used disinfectant and dosage are quicklime 20g/m3 or bleaching powder 2g/m3 or povidone iodine 4.5~7.5mg/m3 (in terms of effective iodine) ). If conditions permit, use EM bacteria, Bacillus and other micro-ecological preparations to regulate water quality, and add immune enhancers such as rhubarb, tea cake, vitamin C and chitosan to the feed to improve the immunity of the shrimp. 5 feeding of bait Feeding of bait is mainly based on commercial feed. The protein content of commercial feed is 26% to 30%, suitable for fresh animal feeds (such as fish meal, snail meat, etc.), as well as plant-based foods (such as wheat, corn, soybean meal and vegetable oil cake). The specific feeding amount should be flexibly controlled according to the amount of shrimp storage, weather and water quality. It should be fed 1 or 2 times a day. The daily feeding amount accounts for 5% to 8% of the total amount of shrimp stored in the field. The main, the amount of feed is about 70% of the daily feed. In autumn and winter, when the water temperature is lower than 12 °C, the feeding is stopped. After the winter, since March of the next year, as the water temperature rises and the K. sinensis out of the hole, the bait can be fed in moderation. The above is all the content of today, yes, do you have this type of breeding mode technology on your side? Everyone is welcome to share and discuss agricultural experience! Source: Guizhou Agricultural Science Author: Zhang Jiahong, Bi Jianhua, Zhu Lingyu Medical Instruments And Equipment Medical Instruments And Equipment,Nucleic Acid Extraction Robo,Nucleic Acid Extraction Instrument,Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Method,Urine Analyzer Jilin Sinoscience Technology Co. LTD , https://www.contoryinstruments.com