Zhuhai Mingke Electronics Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.mingke-tech.com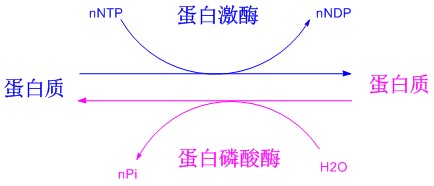
When the monomeric method is modified, the phosphorylated amino acid is difficult to condense with the peptide chain due to the steric hindrance generated by the larger group modified by the side chain, and the subsequent introduction of the amino acid is difficult, especially in the case of containing multiple phosphorylation sites. At the time, the synthesis becomes extremely difficult, and the final product composition is complicated, difficult to separate, and the yield is extremely low. Therefore, when phosphorylation is carried out at multiple sites in the peptide chain, post-phosphorylation can be considered. The synthesis process is mainly to selectively remove the side chain protecting group of the amino acid to be labeled after the end of the peptide synthesis. Thr can be directly reacted with amino acids that are not protected by a side chain. The side chain protecting groups can be quantitatively removed under 1% TFA/DCM conditions. In the post-phosphorylation, bisbenzyl phosphoramidite can be used, and tetrazolium is formed into a phosphoramidite tetrazole reactive intermediate, which is attached to a hydroxyl group, and then oxidized to form a phosphoryl group under a peroxyacid condition to complete the reaction. 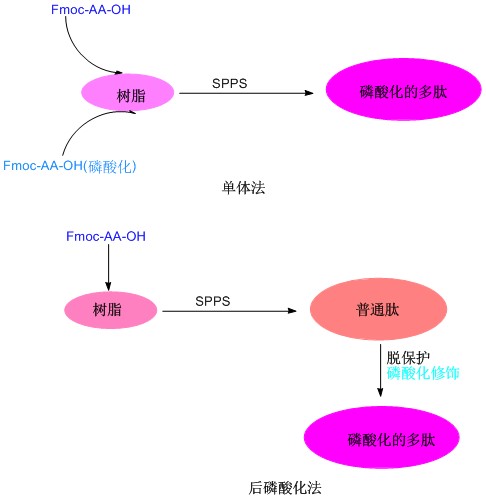
success case:
Sequence NH2-TERD(pS)D(pT)DVEEDSRPPGRPAEVHLERAQPFGFID(pS)D(pS)DAEEEY-CONH2, four phosphorylation sites.
HPLC analysis: 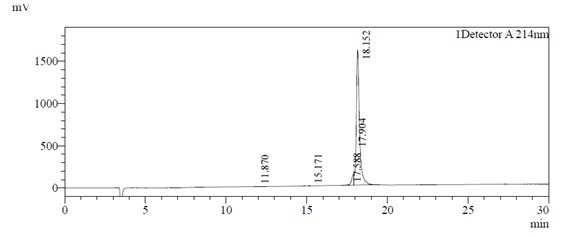
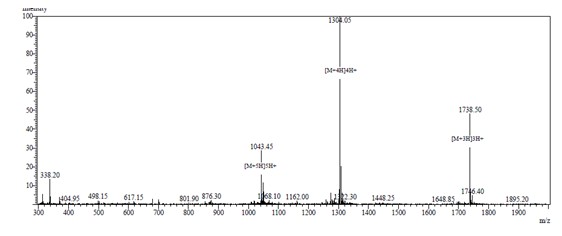
Protein phosphorylation is the most common and most important post-translational modification of proteins in the biological world. It has been regarded by biologists as a dynamic biological regulation process since the 1950s. About one-third of the proteins in cells are thought to be modified by phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of proteins is closely related to a variety of biological processes, such as DNA damage repair, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, and regulation of apoptosis. The study of phosphorylated proteins and peptides can help people explain the mechanism of the above process and further understand the nature of life activities. In recent years, with the continuous development of proteomic technology, research on protein phosphorylation has received more and more attention. We offer peptides with high quality peptides modified with two, three, four, and five phosphorylation sites. With mature synthetic purification technology and an enterprising elite team, Guopeptine has become a trusted peptide supply brand. MS analysis:
The role of protein phosphorylation in cell signal transduction
Phosphorylated polypeptides primarily refer to the modification of a side chain hydroxyl group of the Ser, Tyr and Thr residues in the peptide chain to an acid phosphate polypeptide. Phosphorylation of peptides is an indispensable tool for studying protein phosphorylation processes, so it is important to study the phosphorylation of proteins and peptides and to determine a mature and simple synthetic route. Up to now, the phosphorylation modification of polypeptides mainly includes two methods of post-phosphorylation and monomeric synthesis. Post-phosphorylation is the phosphorylation of the side chain hydroxyl groups of Ser, Tyr or Thr after the peptide sequence is synthesized on the resin; the monomeric law is to introduce the appropriately protected phosphorylated amino acid directly into the polypeptide sequence. The method is simpler than the post-phosphorylation method and has become the main method for phosphorylation of peptides.