Gas chromatography knowledge Gas chromatography (GC) is a major scientific and technological achievement in the 1950s. This is a new separation and analysis technology that has been widely used in industry, agriculture, national defense, construction, and scientific research. Gas chromatography can be divided into gas-solid chromatography and gas-liquid chromatography.
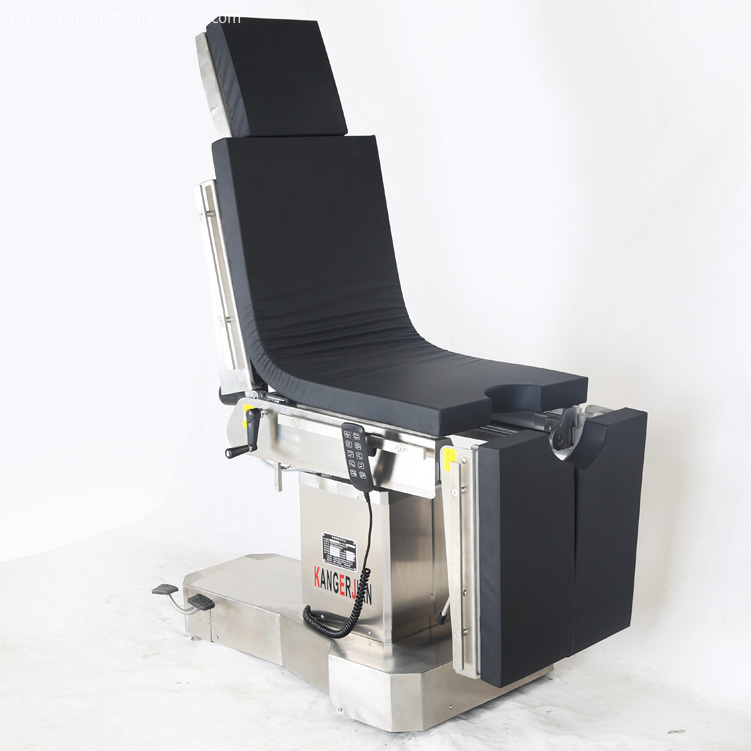
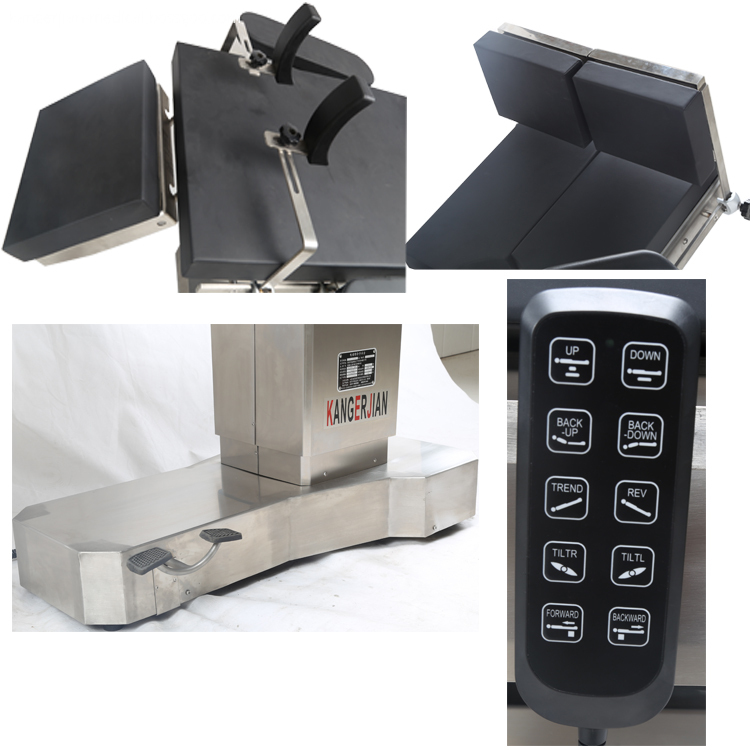
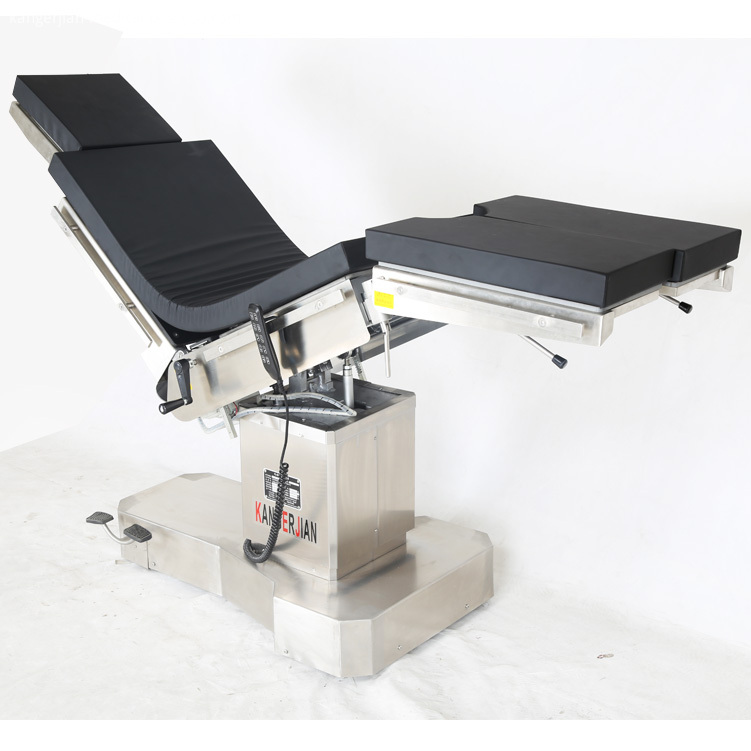
Electric power source Operating Table , selection of Motor push rod power, high quality and reliability. Electric Surgical Table, 2. Use imported gas spring as the manual power source of the operating table, stable performance. Electric OT Table, 3. Operating table using medical-grade 304 stainless steel, more modern, cleaner and more convenient. Integrated operating table, Electric Surgery Table, 4. High-strength stainless steel bottom cover, compressive ability, anti-corrosion, easy to clean. 5 head and leg plate removable, easy to operate, provide more flexible surgical space. Electric Operation Table, 6. Hand control, and has a key switch to prevent misuse. 7. Operating table base has a fixed or mobile function, mobile and flexible, fixed and reliable. 8. Countertop optional built-in waist bridge, gallbladder, kidney and other operations to provide convenience. Hospital integrated operating table, 9. Optional built-in battery to protect the operating table without interruption. 10. Table optional longitudinal translation, to achieve all-C shooting.
Electric Operating Table,Electric Hospital Beds,Electric Medical Operating Table,Medical Electric Operating Table Shandong Kang'erjian Medical Technology Ltd. , https://www.operatingtable.nl
Gas Chromatography Classification Gas chromatography can be divided into gas-solid chromatography and gas-liquid chromatography. The word "gas" in gas-solid chromatography means that the mobile phase is a gas, and the word "solid" means that the stationary phase is a solid substance. For example, activated carbon, silica gel, etc. The word "gas" in gas-liquid chromatography means that the mobile phase is a gas, and the word "liquid" means that the stationary phase is a liquid. For example, a layer of squalane is coated on an inert material diatomaceous earth to separate and measure trace amounts of methane, acetylene, propylene, propane and the like in pure ethylene.
<br> the history of the development of two aspects of the GC chromatogram development and following GC gas chromatography are inextricably linked. The first is the development of gas chromatography separation technology, and the second is the development of other disciplines and technologies. In 1952, James and Martin proposed gas-liquid chromatography and invented the first gas chromatograph detector. This is a titration device attached to the outlet of the packed column to detect the separation of fatty acids. The volume of the solution was plotted against time to obtain an integrated chromatogram. Later, they invented a gas density balance. In 1954 Ray proposed a thermal conductivity meter that opened the era of modern gas chromatograph detectors. From then until 1957, it was a packed column, TCD era. In 1958, Gloay first proposed capillary. In the same year, Mcwillian and Harley invented FID. Lovelock invented the argon ionization detector (AID) to increase the sensitivity of the detection method by two to three orders of magnitude. In the 1960s and 1970s, due to the development of gas chromatography technology, the improvement of column efficiency, the development of environmental science and other disciplines, the requirements of trace analysis were put forward, and some highly sensitive and highly selective detectors appeared one after another. For example, in 1960, Lovelock proposed the electron capture detector (ECD); in 1966, Brody invented the FPD; in 1974, Kolb and Bischoff proposed the electrically heated NPD; in 1976, the US HNU Company introduced the practical window photoionization detector (PID). )Wait. At the same time, due to the development of electronic technology, the original detector has made significant improvements in structure and circuit. For example, the TCD has a balance current, a cross-hot wire temperature, and a temperature-receiving wire temperature detecting circuit; the ECD has a constant frequency variable current, a constant current pulse modulation detecting circuit, etc., thereby improving performance. In the 1980s, due to the rapid and wide application of elastic quartz capillary columns, the requirements for small size, fast response, high sensitivity and good selectivity were proposed for the detector, especially the development of computers and software, so that TCD, FID, ECD, The sensitivity and stability of the NPD and the NPD are greatly improved, and the pool size of the TCD and the ECD is greatly reduced. In the 1990s, due to the rapid development of electronic technology, computers and software, MSD production cost and complexity decreased, as well as stability and durability increased, making it one of the most versatile gas chromatograph detectors. A non-radioactive pulsed discharge electron capture detector (PDECD), a pulsed discharge/ionization ionization detector (PDHID), and a pulsed discharge photoionization detector (PDECD), as well as a pulse discharge detector (PDD) Four years later, the American Varian company introduced a commercial instrument that is 100 times more sensitive than the usual FPD. In addition, the rapid development of rapid separation techniques such as fast GC and full two-dimensional GC has prompted the rapid development of rapid GC detection methods.