Atmospheric PM 2.5 has a small particle size and a large specific surface area. It can adsorb a large amount of toxic substances and can penetrate deep into the lungs, which has a major impact on human health. Epidemiological investigations have shown that PM 2.5 -based airborne particulate contamination can lead to lower respiratory tract infections, trachea, bronchitis and lung cancer, ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and premature death of the population. Occurred, it is more harmful to the elderly, children and people with heart and lung disease.
In recent days, Beijing has been a yellow warning of heavy pollution.
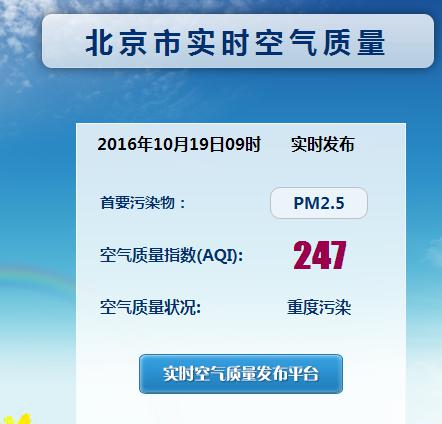
Beijing Environmental Protection Monitoring Center Data
Epidemiological studies on the acute effects of PM 2.5 on health effects have been reported in many domestic literatures reflecting the exposure response of this effect. Such population health effects include total mortality, cardiovascular mortality, respiratory disease mortality, total outpatient rate, cardiovascular disease outpatient rate, internal medicine outpatient rate, total emergency rate, cardiovascular disease emergency rate, total hospital admission rate, Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease admission rate, admission rate of respiratory diseases, incidence of adverse reproductive outcomes, and respiratory symptoms, lung function and immune function changes in the population [1] . The epidemiological study of acute health effects conducted by Chen et al. used a two-stage Bayesian hierarchical model to quantitatively assess the impact of air pollution on the daily mortality of residents in 17 cities in China. The results showed that for every 10 μg/m 3 increase in PM 2.5 , total mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and respiratory disease mortality increased by 0.40% (95% confidence interval: 0.18%, 0.61%), 0.47% ( 95% confidence interval: 0.23%, 0.72%), 0.46% (95 confidence interval: 0.19%, 0.74%) [2] .
Epidemiological studies can only provide a general relationship between particulate exposure and pathogenic outcomes, such as hospitalization rates, associated morbidity, and premature death, but do not address the pathogenic mechanisms of PM 2.5 effects on human health. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a health risk assessment and pathogenic mechanism study of human volunteers or animal PM 2.5 real-time exposure. Research teams such as Harvard University conducted a series of in-depth studies using the self-made PM 2.5 real-time concentrated exposure system, designed as a fixed and mobile PM 2.5 real-time concentrated exposure system. Liver fibrosis [3] , diabetes [4 , 5] , cardiovascular disease (hypertension, cardiovascular, heart disease) [6-8] , metabolic disorders [9] , allergic reactions, asthma [10] , nerves System [11] , lung inflammation [12] , lung cancer [13] and so on. Subjects included human volunteers, sensitive animal models, and concentrated exposure to normal animals. The concentration of PM 2.5 after concentration was extremely high at the highest concentration of 800-900 μg/m 3 . For most studies, the concentration of PM 2.5 after concentration was 100-200 μg/m 3 .
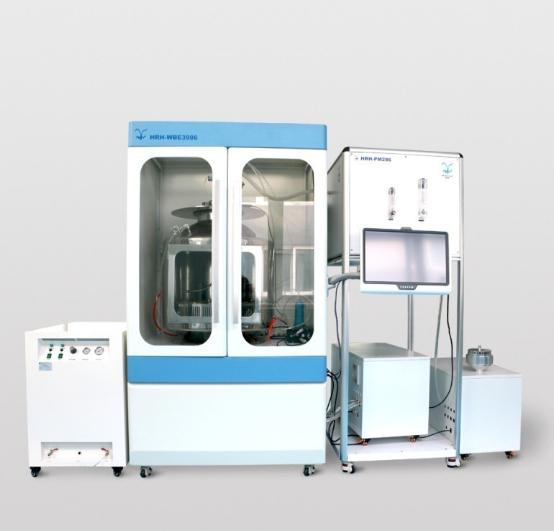

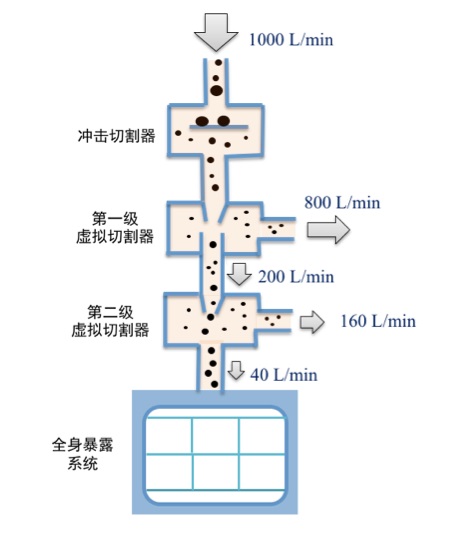
Schematic diagram of PM2.5 real-time online concentrated exposure system
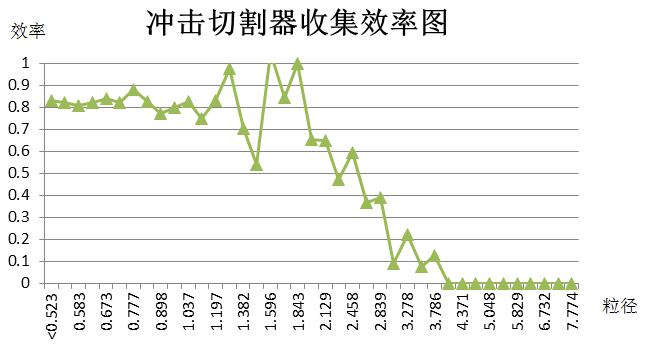
In order to meet the needs of Chinese researchers for PM 2.5 real-time concentrated exposure system, Beijing Huirong and Science and Technology teamed up with China CDC, Military Medical Academy and other experts to develop China's first set of PM 2.5 real-time concentrated exposure system. The PM 2.5 real-time concentrated exposure system mainly includes PM 2.5 sampler, PM 2.5 concentrator, power supply system, flow control system, animal real-time inhalation exposure system, pollution airflow purification system, computer automatic control system, concentration real-time monitoring system, animal environment. Monitoring system and other components. The PM 2.5 real-time sampling and concentration system meets the requirements of the Ministry of Environmental Protection HJ93-2013 for samplers. The animal inhalation exposure system meets the requirements of the OECD for animal inhalation toxic exposure equipment. The system can concentrate 6-10 times of PM 2.5 in the environment, and can conduct acute, subacute, subchronic, and chronic inhalation exposure studies of animals according to different purposes of the experiment.
main reference
[1] Song Donglin. Current Situation and Challenges of China's Haze Weather, Environment and Health Outlook (EHP Chinese website), August 2013.
[2] Chen R, Kan H, Chen B, et al. 2012. Am J Epidemiol 175(11): 1173-1181.
[3] Zheng Z, Zhang X, Wang J, et al. J Hepatol. 2015,63(6):1397-404.
[4] Liu C, Fonken LK, Wang A, et al. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2014, 11:53.
[5] Liu C, Xu X, Bai Y, et al. Environ Health Perspect, 2014, 122: 17–26.
[6] Rao X, Zhong J, Maiseyeu A, et al. Circ Res, 2014, 115(9): 770-80.
[7] Ying Z, Xu X, Bai Y, et al. Environ Health Perspect, 2014, 122: 79–86.
[8] Xu X, Yavar Z, Verdin M, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2010;30:2518-2527.
[9] Mendez R, Zheng Z, Fan Z, et al. Am J Transl Res, 2013;5(2):224-34.
[10] Wagner JG, Morishita M, Keeler GJ, et al. Environ Health, 2012, 11:45.
[11] Fonken LK, Xu X, Weil ZM, et al. Mol Psychiatry, 2011,16(10): 987–973.
[12] Harder SD, Soukup JM, Ghio AJ, Devlin RB, Becker S. Environ Health Perspect, 2001, 109 Suppl 4: 599-604.
[13] Fernanda Alves Cangerana Pereira, Miriam Lemos, Thaı Ìs Mauad, et al. CLINICS, 2011, 66(6): 1051-1054.
Blackhead Suction Tool,Best Blackhead Remover,Electric Blackhead Remover,Best Blackhead Suction Remover
Shenzhen Jie Zhong Lian Investment Co., Ltd. , https://www.szmeizons.com