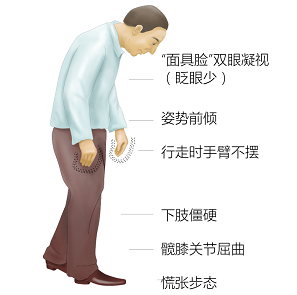
April 11th is the world's Parkinson's disease. In 2017, the world's Parkinson's disease was discovered for 200 years. This year is also the 40th year of Chinese Parkinson's disease. At present, Parkinson's disease has become the "third killer" for middle-aged and elderly people after cancer and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, but the public's understanding of Parkinson's disease is still very low. According to the survey, more than 90% of the public do not understand Parkinson's disease, and more than half of them think that Parkinson's disease is Hawking's "frozen disease"; more than 34% believe that acupuncture can cure Parkinson's disease; more than 93% do not know Pa Surgical treatment of Jinsen's disease; more than 60% of non-neurological surgeons do not understand disease and brain pacemaker surgery. In order to better benefit patients with Parkinson's disease, the Chinese Medical Association Neurology Branch Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Group, the Chinese Medical Association's Neurology Branch Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Committee and Medtronic launched the "Hug Tulip" project. Continuous investment will be made in the fields of professional neuro-internal surgeon training, patient disease science education, and popular disease knowledge science communication. What is the story of Parkinson's disease and tulips? Originally in 2005, international organizations selected red tulips as a symbol of Parkinson's disease because a Dutch horticulturist, J.W.S. Van der Wereld, cultivated the cultivar he cultivated in 1981. Named "James Parkinson Tulip". Today, this tulip is designated as a marker for International Parkinson's Disease Day and is widely used by international Parkinson's disease organizations. According to Prof. Chen Shengdi, the leader of the Department of Neurology of the Chinese Medical Association, and the director of the Department of Neurology of Ruijin Hospital, Professor Hu Shengdi introduced the “Hug Tulip†project. In the past five years, he has carried out more than 500 clinical science education for patients in all parts of the country. Train more than 5,000 neurosurgical specialists; and continue to conduct disease and treatment popular science activities every year, aiming to improve public awareness of Parkinson's disease, improve the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson's disease professionals, and better provide patients with Long-term disease management program. Hand shake, tremor, stiffness, slow action, alert to the attack of Parkinson's disease "200 years later, the public's awareness of Parkinson's disease is still limited or even misunderstood, which makes me feel very sad, and let our specialists of Parkinson's disease feel a long way to go." Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Wang Jian, deputy director of the Department of Neurology, and deputy head of the Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Group of the Shanghai Medical Association's Neurology Committee. Disposable Piercing Guide - WPTC12
Disposable surgical instruments are single-use medical devices that are used during surgery and discarded after use. Some examples of disposable surgical instruments include:
1. Scalpel 2. Tweezers 3. Scissors 4. Needle 5. Suture material 6. Surgical drapes 7. Surgical masks 8. Surgical gloves 9. Ironing pen 10. Trocar and cannula.
10. Laparoscopic instruments: Used for minimally invasive surgeries, these instruments include a camera and specialized tools for performing surgery through small incisions.
Radial Artery Compression Devices,Outlet Radial Artery Compression Device,Disposable Radial Artery Compression Device,Medical Consumables Tourniquet Changzhou Weipu Medical Devices Co., Ltd. , https://www.cnweipumedical.com
2. Forceps: A tool used for grasping and holding tissues or organs during surgery.
3. Retractors: Surgical instruments used to hold open incisions or wounds to provide better visibility for the surgeon.
4. Scissors: Used for cutting tissues and sutures during surgery.
5. Hemostats: Used to clamp blood vessels and prevent bleeding during surgery.
6. Suction devices: Used to remove fluids or debris from the surgical site.
7. Needles: Used to suture or stitch wounds.
8. Electrocautery: A tool that uses an electrical current to cut or coagulate tissues during surgery.
9. Endoscopes: Used for minimally invasive surgeries, these instruments allow the surgeon to see inside the body without making large incisions.